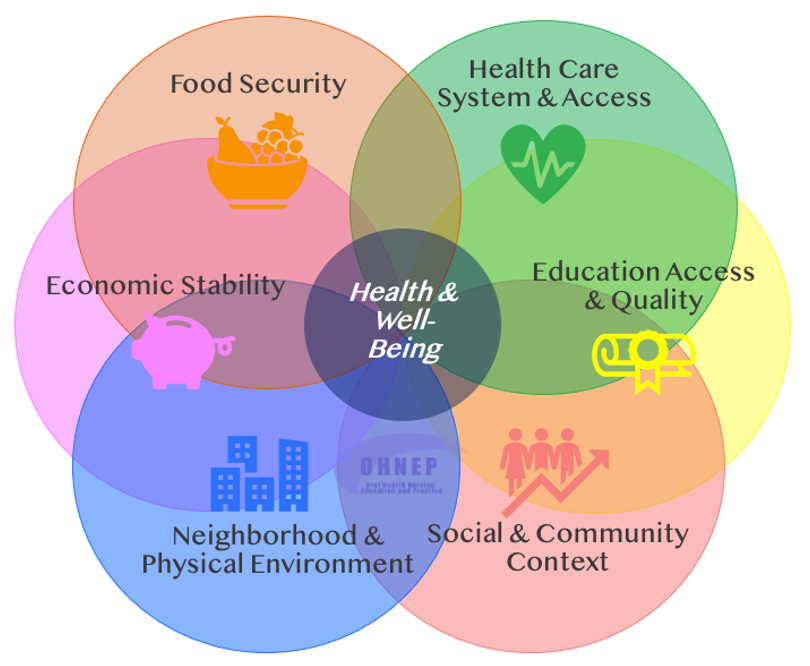
Social determinants of health (SDOH) are the conditions in the environments where people are born, live, learn, work, play, worship, and age that affect a wide range of health, functioning, and quality-of-life outcomes and risks. Promoting oral health and preventing oral disease in our communities is a national and global population health issue that disproportionally impacts vulnerable populations affected by the social determinants of health. The social determinants of health that contribute to oral health disparities include:
- poor nutrition related to food insecurity
- insufficient fluoride exposure
- poor oral hygiene
- inappropriate methods for feeding infants
- adolescent use of tobacco and alcohol
- limited availability and accessibility of oral health services